Which kind of headphones would be most suitable for me? Which type of headphone should I purchase?
It’s not that difficult — simply seeking “headphones” on a search site or an online retailer could make the process more complicated than it was when you first began with it, as the methods you can limit your headphone search can be quite complex and, ultimately, chaotic.
Full list of Headphone Classification Guide
We covered this in the headphone guide to assist you with tips and recommendations to select which is the “best pair”,
we focused on those “types” only briefly.
Today , we went into more depth to help know what these “ear”, “in””over”, and “over” superlatives mean when they refer to the capabilities of headphones and how they fit. Let’s dive into it!
Explained What are the different types of Headphones?
Which kind of headphones would be most suitable for me? What type of headphones do I need to buy? It’s not that difficult — simply looking for “headphones” on a search engine or on a shopping website can make the search harder than it was when you first began with it, as the methods you can limit your headphone search can be quite complex and, ultimately, complicated. We covered this in the guides to headphones to help you make suggestions and help you choose your “best pair”, we discussed those “types” only briefly. Today , we went into more depth to help you know what these “ear”, “in””over”, and “over” superlatives mean when it comes to headphone features and how they fit. Let’s get started!
kinds of headphones.
Closed-Back Headphones
The well-loved closed back headphones are an excellent kind of headphone for those who wish to block out any outside noises when wearing the headphones regardless of their intention for use. The design eliminates any noise surrounding you , ensuring that the music completely free of external interference regardless of your surroundings, and also provides a completely isolated audio experience that ensures it is only youcan hear the sounds that you desire to hear. These headphones are ideal for those looking to be able to hear every single aspect of the music they listen to, and completely immerse their ears in the experience.
The type of headphone described above is very popular and used by musicians recording in studio settings like the numerous models of Studio headphones because of their ability to block out external noises while focusing on the notes of the singer or instrument. They also have virtually zero noise loss, meaning that very little sound is lost to the outside surroundings (any lost sound that is leaking to the microphone can begin to obstruct the track Think of an artist listening to instruments through the headphones as they singit’s not a good idea to let this faint sound to be heard within the track, either). In addition to musicians closed-back headphones are great for those who want an intimate listening experience, or for an environment that you don’t wish to disrupt the other listeners.
Closed-back headphones are available in the over-ear design that completely covers the ear, as well as the more compact on-ear model that sits over the ear (both explained in a more later). In terms of style, they’re generally larger than other headphones, and are worn on top of the head. However, for those who don’t mind the size of these headphones, they will deliver superior sound quality with a variety of uses for nearly all headphone users, providing us a wide range of design options and being the first item in our list.
Open-Back Headphones
The well-known open-back headphones vs. closed-back headphone will be a factor in this case. Based on the title, open-back headphones aren’t “closed” and instead have “open” ear cups that let some sound out into the surrounding (on the basis of purpose!). The result is a sound that is more “airy and open sound” which is similar to hearing the sound of speakers inside the room (if we were to pick an analogy that is acceptable) rather than listening to a completely silenced sound emanating in closed-back headsets. Why would anyone need this kind of airy open sound, with small amount of audio coming through the ear cups? What’s the reason?
This is the most popular choice for those mix and master at studios. Because of the open design this leakage is often appreciated by audio engineers since it lets the mix be accurate and not suffer from building up of certain frequencies that typically occurs when using closed-back headphones. As someone who’s involved with mastering and mixing needs precision and “flat sound” with no extras, it gives them greater confidence and flexibility to be able to believe the sound they’re hearing. The closed-back headphones, while great for sound isolation but will begin to retain lower frequencies within the earcups after time (which many people appreciate when they’re enjoying their music for a long time).
A lot of audiophiles opt for open-back headphones, even though they’re not recording or mixing in a professional studio, they need that genuine flat sound, so that they can get exactly what the artist wanted the listener to hear. If you’re not interested in anyone to hear the audio or the music you’re listening to, these aren’t best suited for you. If you’re not worried about others who are around you hearing the music, this design is ideal. Also, there is less pressure that is created by this type of headphones. This makes the headphones more comfortable for extended durations of time. Open-back headphones, which are similar to closed-back headphones, are available in an over-the-ear model or the smaller on-ear design also. Additionally, there is a uncommon models called semi-open headphones that, as you’ve guessed they blend both styles by having an appearance that is just a little open , allowing a some sound leakage, but they also provide sound isolation at the while.
*Note: We own an closed and open backs, and switch them out based on the application. We also use closed for mixing occasions, just in case we need to have a slightly different view. We suggest using both when making your own mix.
On-Ear Headphones
Like the name suggests, on-ear headphones can be worn on top of the head and sit on the top of the ear. At first, we were confused about on-ear headphones vs. headphones that are over-ear (listed in the next section) To summarize our findings take it as that: on-ear headphones are a bit less sized (nearly similar to the dimensions of an own ear) are positioned well on top while over-ear headphones are smaller size, meaning that they can cover your ears in a cushion which surrounds the ears. What is the reason for these two different styles exist?
Also known as Supra-aural headphone The on-ear style is somewhat like open-back style headphones, that allow some sounds from the outside to go out (as well as in) instead of the over-the-ear model, which is better in blocking out sounds from outside for those who are worried about the phrase “sound isolation”. These headphones are generally comfortable and won’t cause sweating more than the headphones that sit on your ears. They hang on to your ears,, therefore it’s crucial to purchase an earphone that is comfortable and doesn’t make your ears feel too strained (or at the very least, as much as over-ear, closed-back headphones, although certain people prefer this sensation).
They also weigh less than the over-the-ear models, which means less pressure is placed on the top part of the ear that sits upon your head. The models that are over-the-ear can differ greatly in terms of performance, however should you opt for one of the better models, they will be able to meet the areas you care most about: the sound high-quality and comfortable. There are a variety of models available in this category with distinct features, but in general, this is likely to be the most active in the sense that it has all the features. It’s all about your personal preferences in the end and many will disagree on “sound quality” and “comfort” (two very subjective terms for headphone descriptions) for both .
Over-Ear Headphones
As shown in the picture, over-ear headphones (or sometimes technically, known in the form of ‘ circumaural‘) sit on the top of your head in addition to “over” (on, as well as around our ear cartilages , ensuring that the entire ear can be “cupped”) to focus on the isolation of sound. These headphones are the most effective model to reduce noise as they create a cosy space with you as well as the music that you are listening to. They’re very effective at restricting noise leakage, which allows the music that you’re listening to in and lets the sound of the surroundings to be heard. There is a possibility of getting over-ear models that have an open-back which allows them to breathe and allow sound to flow in and out. But, these models are typically closed-back because they are favored for their ability to cancel out noise isolation, as well as the superior sound quality.
They’re very comfortable (especially in the case of higher-end models certain cups are made of leather or velvet) and won’t smack your ears like the models that are on-ear. However, they are likely to make you sweat as there isn’t much air circulation in or out. They also are the most bulky kind of headphones on the market and if you’re looking to reduce space, these might not be suitable for you. Other people will prefer these headphones that are more bulky and want that tight, heavy, and comfortable design (like pillows that are pressed to the back of the head).
They tend to be larger than the other types and can cause discomfort to your ears and head while wearing them for prolonged durations, particularly when you are in the studio, or gaming, for instance. But, if you have the space and aren’t concerned about the size, you’ll be in a position to shut the world away and enjoy the music you love in a clean and intimate setting.
In-Ear Headphones
Let’s talk about portability, flexibility and ease of use. The most convenient and portable design of headphone models currently available is the in-ear headphone and, as they’re sometimes calledas ‘ canalphones‘. They are among the most popular styles of the market for headphones due to their convenience of using them when you’re not a professional, semi-pro, or home engineer or studio artist. With the advancement of technology, you can get better audio quality with smaller units and smaller models, these have been able to swiftly advance to compete with larger over-ear and on-ear models. Instead of earbuds that rest on the outer ridges of your ear They are a bit deeper into that canal (see the source of the name from?) to sit inside your ear and move closer to your important eardrums.
The advantages of this are certain aspects that include comfort (for certain, at the very the very least) as well as sound isolation and even sound quality. Consider them as the closed-back versions of the portable headphones. These headphones typically have minimal sound leakage, thereby keeping the sound inside your ear while keeping outside noises out. In-ear headphones usually come with a silicone earpiece to protect your ears and provide more comfort. This ear tip covers the ear canal, allowing the audio from the headphones to be absorbed right into the ear, while keeping the majority of sound from the outside out.
For those who prefer listening to music at leisure and in the car in their car, on the move or in the gym, these are your ideal choice. The style is able to provide outstanding sound quality based on the model and is popular with a large number of people who use them — the majority of us own one (or 2) headphones that are suitable for both desk and music listening, and using earbuds for the aforementioned occasions during our day-to-day lives.
A minor concern for those who use it is the possibility that this design could be hazardous to your ears as they’re directly inside the ear canal, but with the security they provide us, and unless you crank up the volume as loudly as you can using headphones it’s safe. Hearing harm is caused by volume of the sound and not the distance of the sound to the ear, so If the volume is kept at a moderate level, there’s no reason to worry about in the final. It is true that AirPods count as in-ear headphone!
Earbuds
Do you think earbuds are the same kind of headphones that we previously mentioned? Take a second as we present to you the headphones for earbuds and. the in-ear headphone debate. Like we’ve mentioned before, earbuds in contrast to in-ear headphones can be described as small speakers that sit on the ear’s outer. The most well-known and widely used style of earbuds are the white earbuds apple offers in their products. they’re not as sleek of a shape and aren’t able to penetrate your canal as deeply as the other models, but they’re just larger circles that are pressed against the ear’s surface. The style of earbuds does not penetrate the ear canal, but instead rests on the ear’s outer surface that allows greater sound coming from the external surroundings to be absorbed. They permit more airflow than in-ear models and offer some advantages that we’ve observed and sound that is more “flat” sound, perhaps “safer” (for some) and possibly more comfortable for you if aren’t averse to the noise that in-ear headphones provide.
Earbuds are easily mobile and compact like in-ear headphones, however they struggle to achieve real sound isolation because of the size of the speaker. The model that you choose certain models that are more expensive have advanced technology that can enhance the sound precision and quality, however the primary benefit of the earbuds is their dimensions. We’re sorry to offer this advice, but it’ll be dependent on the individual. If we had to offer a recommendation that we would rather use in-ear headphones (especially in the gym and we’ve had headphones fall out of our ears several times when we were working out or running). They don’t hold the ear as well as the headphones in the ear and can easily be a bit loose.
Earbuds generally come in a single size fits all, which causes them to be uncomfortable for some types of ear, but certain brands offer different sizes of ear tips for users to change and adapt your own. If you’re seeking high-quality audio it’s difficult for this type of headphone to be competitive with other categories of headphone but if you’re looking for an ultra-compact model that’s lightweight to carry around, then they could be the right choice for you.
Bluetooth Headphones
Wireless electronics are a common feature in the world today. So what is it with the wireless headsets? What kind of headphones are with wireless technology? For starters, they are can be used to provide wireless connectivity to devices using the radio transmitter (RF) (RF) — which is good old sound waves carried through the air and into receivers. But, it’s almost out of use at present. This is due to Bluetooth technology which permits devices to be connected wirelessly by using radio waves. However they’re on their own channel instead of having to connect through a particular number of frequencies (which often caused interruptions when using radios that are extremely out of date).
The technology is rapidly evolving particularly in the field of music, but not just in the music industry (we can see all kinds of Bluetooth electronic devices today). Headphones that use Bluetooth technology include a small computer chip within they that lets you connect to the device you’re playing music from. If you connect headphones using Bluetooth you can listen to the same audio similar to normal headphones, but without the burden of cords. The advantages are pretty obvious regardless of whether you are at the gym, in transit at home, all other situations that you do not want to be concerned about those annoying things.
Additionally The audio high-quality of Bluetooth headphones is similar to the corded models and you won’t have any loss in sound quality simply because you’ve lost the cord. There are some who complain about “lag” or “delay” during the transmission process, which is in reality true. However, it’s not an issue who are recording, producing and mixing your music (in this case, go with wired, no matter what).
At the moment, these headphones are typically higher priced than corded ones since this technology is still “new” (and of course it costs a little more to manufacture with the chip in the headphone). The best part is that every type of headphone include on-ear models, Bluetooth earbuds wireless, Bluetooth over-ear along with Bluetooth headphones that are on-ear are readily available (those guides might be helpful should you be interested). One drawback of Bluetooth headphones is that they need charging. As opposed to corded headphones that operate on the power of batteries in the device connected, Bluetooth models need to be charged before pairing and pair with the device you’re using. If you’re not afraid to recharge them regularly and have some cash to spare, Bluetooth models are perfect to free you from the cord!
Noise-Cancelling Headphones
We’ve heard the “sound isolation” phrase used to refer to higher-end headphones in the field of marketing you know? How is the sound cancelling headset name? Let’s look at what it signifies. With a special technology integrated they actually reduce the sound you hear from your surroundings , creating an environment that is quiet enough to listen to music, or listening. The way in which the small internal engine accomplishes this is by analyzing low frequencies in the surrounding (there’s an actual microphone attached the outside of the ears) and making an equal and opposite frequency which cancels out the sound that the microphone detects. The sound is eliminated before it even reaches the earpads in order to be absorbed into your sound mix. For sounds with higher frequencies generally, models that have noise cancellation models feature soundproofing which blocks many of the higher frequency sounds, or any combination of these two methods. Check out the noise isolation in comparison to. noise cancellation article to get more information on these technical terms that are frequently switched.
The category of headphones has become popular during air travel due to the fact that it blocks out sounds of other passengers as well as the high frequency of the aircraft’s engine. But, this type of headphones can be useful for a variety of applications outside of the plane also — really all uses you can imagine, aside from engineering or music production however you want. They’re ideal in any scenario in which you’d like to block out all background noises, particularly in areas which are “noisier” than others. By blocking out the noise around you they allow you to listen to music and not be distracted by the surrounding noise. Even though many in-ear or earbud models are typically constructed using NC technology, combining it with over-ear, closed-back headphones gives the best experience in blocking out the world’s exterior, ambient noises.
Full List: Headphone/Earphone Specifications w/ Examples
What are the specifications for headphones? Headphones specifications, shown on specifications/datasheets, are pieces of information that tell us the electrical, mechanical, acoustic and physical characteristics of a pair of headphones (or earphones) and how the headphones perform under normal circumstances.
Specifications for Headphones
Headphones are a complex set of transducers that can be described in a variety of ways.
I’ll list every possible specification that can be found on datasheets for headphones or manuals, as well as selling pages. Each specification will be explained briefly and include hyperlinks to more detailed articles in the event that they are appropriate. I will also provide actual examples of the headphones with the specs mentioned.
To give real-world instances of every specification I’ve gathered a collection of datasheets/product pages from certain manufacturers of headphone kinds. These are the examples below:
The links included will take you to the bottom of the article in which each headphone is explained in more depth, and all of the specifications listed to serve as a reference.
The Headphones Specifications List Headphones Specifications
Model
The specification simply specifies what the manufacturer is of the particular headphone. This specification is unnecessary since the exact name of the headphone is clearly mentioned in other places (like on the top of the specifications sheet).
Wearing Style
The style of wearing of the headphones is a rather redundant physical description. It is a reference to how the headphone is to be worn.
In general, this distinguishes the headband model (headphones) from models with in-ear connectors (earphones). It could also be referring to headphones that are on or over-ear models.
Contact Pressure
The headphones are worn on the head, and they apply a certain amount of pressure to the ear or on our necks. Certain manufacturers go through the hassle of determining the pressure that the headphones apply to our head when it is worn.
To fully comprehend this specification it is important to understand the method of measurement. Consider how wide the headphones spreadout, as an instance.
Ear Coupling
Diaphragms for headphones change the sound pressure and oscillate when they do this.
Human eardrums also function as membranes. They change shape in response to changes in sound pressure.
In forming the headphone driver diaphragm and eardrum, it creates an eardrum-to-ear mechanical coupling, which greatly enhances the ability of the driver to touch the ear.
It is a method of seal (known by the term coupling) is achieved through in-ear headphones that connect to the canal of the ear. It is also possible to achieve coupling using circumaural (over-ear) headphones which completely cover and seal out the entire ear.
Drivers
This specification provides information about the drivers of the headphone.
The drivers are components of the headphone’s transducer that convert audio signals to the sound we can hear. According to this definition they are essential and are worth knowing about.
The term”driver” is typically applied to headphones that are electrodynamic (they represent by far the most well-known kind) but it is also applicable to different kinds (electrostatic and planar magnetic for instance).
The driver specification can provide information on the kind of driver as well as the size of the driver (the diameter of the driver’s diaphragm) or the voice coil and magnet materials.
Materials
The specification for materials may include or not mention the specific materials listed in the driver specifications. All depends on the specification that the manufacturer decides to include in their datasheet.
Materials generally reveal the materials used in headphones’ ear pads and cups, and may also include cables, the band and driver materials.
Antenna
Wireless headphones are equipped with receivers and, consequently, will likely have antennae. The antenna specifications are not common however, it reveals the shape and/or the material that the antenna is made of.
Jack/Plug (Connection)
The connection between the jack and plug tells us that the headphones are compatible with regard to the various connections of the headphone. It also tells us in a way that we’ll require adapters or if adapters even function.
For headphones with wires the plug is the final connector on the cable.
Certain headphones have detachable cables. So this description will reveal the headphone’s jack end. That is, which cable will plug into the headphone?
Headphone Jacks are typically 3.5mm or 6.35mm but they could be 2.5mm or 4.4mm in certain cases.
Connection Cable
The connection cable is the detachable cord that is to be used to connect the headphone an output of the headphone.
In most instances, this description will only provide the length of the cable and whether it’s normal (straight) or coils.
Other data sheets provide the wiring inside, however this isn’t very common.
The specifications for the cable are more crucial in headsets since the cable needs to carry an audio signal in addition to being compatible with the connected device.
Electrostatic headphones as well as other kinds that require specific headphones typically have cables that are typically exclusive and of high-quality. The specifications of their cables are, therefore, crucial to know.
Weight
Headphones are intended to be worn over our heads. So the headphone’s weight is a major factor in our experience.
Specifications for weight typically take two kinds:
- The headphone’s weight is determined by its cable.
- The weight of the headphone is not as much the cable.
Transducer Principle/Type
The specifications for the transducer’s principle (often referred to as “type”) tells us how the headphone actually generated sound using audio signals.
It is possible to make certain assumptions about the various types of transducers It is helpful to identify the type of headphone we’re considering while looking at a specification sheet.
The dynamic moving-coil headphone transducer as an example is the most well-known and that the other specifications to permit an easy comparison with other dynamic headphones.
Different types of transducers, such as the electrostatic headphone will function differently. It is expected for the headphones to have a wide range of frequencies, sensitivity, and impedance responses. Also, they’ll have distinct cables because they are connected to amplifiers that are specifically designed for them.
Moving-coil dynamic headphones are characterized by their moving-coil driver. They transform sounds into audio waves through electromagnetism (electromagnetism). The HPs create sound through diaphragms and conductive coils which move when they hear audio signals.
These headphones turn audio frequencies to sound waves using electromagnetic principles. The drivers of their planar design are constructed with electrical conductors that are thin and placed in a diaphragm which oscillates between two arrays of magnetics.
Electrostatic headphones transform sounds into audio. They rely using electrostatic principles. The audio signals create different electric fields within the driver, which move the diaphragm. They also produce sound waves.
Balanced Armature (BA) models are based using electromagnetic principles and employ BA drivers which work using an armature that is that is wound around an armature moveable connected to diaphragm.
Bone conduction headphones transform the audio signal into physical vibrations. They accomplish this by using piezoelectric drivers that are connected to the user’s jaw or cheekbones. The vibrations reach the inner ear, and are perceived as sound.
Frequency Response
The frequency response of headphones is the specific sensitivity to frequency that the output of the headphones.
This specification describes the range of frequencies that the headphone can be capable of reproducing sound.
It is important to note that sound is defined as a frequency range 20 Hz – 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. This is the limit of what we can hear (though hearing loss can reduce the range).
A lot of manufacturers describe their frequency response in a spectrum from low to high but do not specify the tolerance. However the specifications are essentially inaccessible to the user in the form of a datasheet.
A tolerance of +3 dB is excellent. It indicates that the headphones can deliver frequencies within their range , with a an maximum of +3 dB within their band.
In some cases we might find the frequency response graph which will provide a graph of the sensitivity of the headphone at every frequency. If you’re looking for frequency response graphs specific to headphones, you should check out third-party test tools such as Fidelity or Inner Fidelity rather than the specifications from the manufacturer.
Sensitivity/Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
The sensitivity of headphones is a term that refers to the ability of a driver’s ability to convert one’s electrical sound signal to sound. This is expressed in terms of dB SPL (decibels of sound pressure) in units in power (typically 1 milliwatt) or in other cases the unit of power (typically 1. Volt) in the direction of the origin with a frequency of 1 kHz.
A headphone with more sensitivity produces higher levels of audio at any given signal at a certain level.
The majority of earphones are said to be sensitive within the range of between 80 and 120 dB SPL/mW. the sensitivity ratings of headphones typically vary between 90 dB and 100 dB SPL/mW. Of of course, there are exceptions that go beyond these limits.
Maximum Sound Pressure
The highest sound pressure of a headphone is the point at which the output will begin to distort.
Sound pressure is typically measured in the earcup or near to the transducer component (where our ears are). The measurement is usually done in a specific frequency, and measured at a specific amount of harmonic distortion of an output sound signal.
Make sure you know how the maximum SPL is measured to comprehend this particular specification.
Total Harmonic Distortion
THD is the term used to describe total harmonic distortion. (THD) is the measurement of the harmonic distortion of the audio signal in terms of percentage of cumulative overtones that are added to the fundamental frequency. It can be measured using the use of a sine wave.
This is a more popular (and easy to comprehend) method of stating the maximum pressure.
0.5 percent THD is the most common threshold for measuring the maximum sound pressure. That is the highest sound pressure of the headphone will be at the point that 0.5 percent (or any other value that is stated) THD is measured in the output.
The level of sound pressure is recorded (typically as dB, or SPL) at a specific THD.
Impedance
Impedance in the headphone is the term used to describe the inherent resistance of the circuitry in the headphone with respect to currents of electricity. Since the headphones form circuits that connect to an audio source and the impedance determines how much power (audio audio signal) transfer and the quality and the amplitude of the sound.
A perfect voltage transfer (audio transmission of signals) requires that the impedance of the source (of the amplifier for headphones, or any other headphone connector) be significantly smaller (ideally at least a tenth) of the impedance of the headphone.
Reduced impedance of the source also increases the damping effect that is, the headphone amplifier has more control over the movements of the driver. This can lead to greater accuracy and less distortion inside the headphone.
Impedance is frequency dependent and frequently is significantly different depending on the frequency response of the headphone.
However, manufacturers of headphones typically offer a minimal (average) amount of their headphone impedance specs.
Third-party testers such as the Inner Fidelity will provide more details about the real frequency-dependent impedance of the headphone.
Load Rating
A load rating a unique design feature provided by Sennheiser for its headphones.
While Sennheiser doesn’t provide a reason for the specification, we presume that it’s the capacity for power handling that the headphones have. It’s the power level at which the driver will cease to function (the coil melts or the motor may over-extend).
This is a typical design for passive loudspeakers which are required to be coupled with suitable amplifiers, but not for headphones.
Driver Matched dB
The headphones are built with two drivers that can accommodate 2 ears.
The drivers are generally identical, however there is a chance that some differences could be observed during the manufacturing process.
The driver-matched dB specifications refers to the greatest level of differences permitted between drivers during quality control. It is typically determined as a ratio in decibels.
The majority of brands do not have this feature because they are reputable brands that are able to be relied upon to test their headphones thoroughly to ensure that each driver is operating at exactly the identical (or nearly the exact) degree.
Left & Right Identification
The headphones fit across the ears of both and have been constructed using a left side and a a right side.
There should be a label on every pair of headphones to indicate which side is worn over each ear.
Sometimes, manufacturers add this information to the specification sheet.
Left and Right Identification“L” along with “R” identified on the arch arrangement (inside of the spring in your head) Cables for the left and right channels are identified with an uniline. On the right side, it is identified by the drawn line.
Noise Isolation
Noise isolation is the measurement of the amount of passive sound cancellation headphones can provide when they are worn correctly.
Passive noise cancellation refers to the physical blockage of audio from entering your ear.
The concept of noise isolation can be described as a uncommon feature and is usually measured in decibels negative to indicate how more quiet the earphones/headphones can make the outside ambient.
Noise-Cancelling Specifications
The phrase “noise-cancelling headphone” means there is active noise cancellation taking place inside the headphone.
There are microphones in the headphone to capture the surroundings. The headphone then uses the noise from the environment to block out the actual sound of the surroundings through playing back out of phase at the correct volume.
As you’d imagine there are many aspects to be considered when talking about an active noise-cancelling (ANC) system. Certain of these information are provided in the specifications sheet of the headphone.
This specification provides us with insight into how the noise cancellation circuit functions. In many instances (as as in this Sony example) it will inform us about the specific technology that is used for this ANC circuit.
Microphone
There are many headsets that include headphones and microphones. A lot of earphones and wireless headsets come with microphones (for the use of telephony as well as active noise-cancellation).
The specifications for microphones in the datasheet for a headphone provide information about the microphone in the headphone or headset.
Common microphone specifications include:
- Type (Element)
- Impedance
- Frequency Response
- Polar Pattern
- Sensitivity
Type (Element)
A microphone’s type, (also known as “element” specification generally refers to the microphone transducer that is used in headsets or headphones.
The microphone transducers function similar to headphone transducers, but in reverse. The microphone transforms sound waves into audio signals. However, the mechanisms of the various microphone capsules are like headphone drivers.
While there are many types of microphones but the two most commonly used that we’ll encounter in the design of headphone are the dynamic with moving coil and electret condenser.
Impedance
The impedance of microphones is like the impedance of a headphone. It’s the opposing force to the signals flowing through an output microphone.
Microphones are thought to be the source of their connections, therefore, to ensure optimal signal transmission their impedances need to be significantly less than the load impedance they’re driving.
Keep in mind that drivers for headphones act as loads, and therefore need a higher impedance to ensure optimal signal transmission to the point of origin. Microphones require the reverse.
As you could be able to guess from our earlier article on the headphone’s impedance, the microphone’s impedance is frequency dependent but don’t be expecting any elaborate graphs. The actual microphone impedance will be shown in the event that it is listed.
Frequency Response
The frequency response of a microphone refers to the frequency specific output sensitivity the microphone. It reveals the output levels of the audio and sound frequencies that a microphone can reproduce.
Frequency responses are defined by frequency ranges. Again, don’t think you will get a full graph. It is possible to consider ourselves lucky in the event that we obtain a tolerable (+/- the dB ) rating.
Polar Pattern
Polar patterns are an indication of the directional sensitivity of a microphone to the pressure of sound. In terms of polar patterns, they reveal the direction(s) the microphone is at ease with sound and in which direction(s) the microphone can reject sound.
There are numerous different polar patterns, but headphones and headset mics are usually an omnidirectional or cardioid variant of hypercardioid or supercardioid.
Sensitivity
Microphone sensitivity is a measure of a microphone’s effectiveness as an instrument for transducing (how it can convert acoustic energy into electric energy). The sensitivity of a microphone is measured by its output voltage (audio signal strength) with respect to the level of sound pressure that it is exposed to.
Sensitivity ratings for headphones could be measured from a standard conversational position using a single-frequency tone or other method. Find out the method used by each manufacturer to measure sensitiveness to get a full understanding of what the specs are telling us.
Bluetooth Specifications
There are many wireless Bluetooth headphones available at present.
Although it’s easy to create (pair) Bluetooth devices, there’s actually a lot of technical details that go into the specifics of how a Bluetooth speaker is able to receive data.
Thus there are the majority of Bluetooth headphones come with a separate section in their specifications which gives the information regarding the Bluetooth connectivity.
Bluetooth Bluetooth specifications are:
- Version
- Compatible Profiles
- Compatible Codecs
- The Range
Bluetooth specifications also include details about:
- For input rating:
- The Battery Status
- Multipoint Pairing:
- NFC:
- Protected Content Supported:
Version
Bluetooth is a Bluetooth protocol is continuously getting improved with frequent release of the latest version.
Each new version builds upon the previous one, adding more capabilities and improved efficiency, while remaining fully backwards compatible.
Two Bluetooth devices of different versions of Bluetooth can be linked with limited functionality of the older version.
Compatible Profiles
Bluetooth profiles define the type of data that can be transferred via Bluetooth technology.
In order for the two Bluetooth devices to work they must have the identical profiles.
Each profile comes with its own list of codecs which it utilizes to exchange data.
Compatible Codecs
The term”codec” stands for coder-decoder. Bluetooth utilizes codecs to format the audio for wireless transmission and later decoding inside the headphones itself.
Range
The Bluetooth range specification is the distance that can be spanned between the headphone’s associated device. In excess of this distance can result in a miscommunication between devices.
Battery Specifications
The wireless headphones run on batteries. Some headphones that have active circuits can be powered by batteries instead of the power supply unit.
Instead of getting into the details about every detail instead, let’s run through the most common specifications for batteries:
- TypeThe sort of battery.
- Life/Playtime:How long the battery will last on a fully charged under normal conditions.
- Standing timeHow how long will the battery run at fully charged while headphones are turned on but not in use.
- Charging timeThe length of time that it requires for the battery to charge between 0% and 100 percent.
- Port for charging:The kind of connector that is used to charge the headphone.
- Replacement/disposal: Information on how to replace and/or dispose of the battery.
Electrostatic Capacitance
Electrostatic headphones utilize electrostatic transducer elements. Electrostatic headphone transducers are efficiently designed as a moveable diaphragm that is electrically charged and that is sandwiched between a massive capacitor that is a parallel plate.
The capacitor is characterized by an inherent capacitance which influences its charge overall as well as the voltage required to charge it and the amount of gain needed to increase the signal from the headphone in order to power the headphone transducer correctly.
Controls
Controls are any additional dials, buttons or voice commands that enable or disable certain features of the headphone.
Water Resistance
The name implies that the specifications for water resistance give us the idea as to how headphones will perform in humid or wet conditions.
The specification is usually delivered in the form of the IP rating.
IP code (Ingress Protection Code) IP code (Ingress Protection code) is a measure as well as a classification for the amount of protection provided by the mechanical enclosures and casings for electrical against dust, intrusion, accidental contact and water.
The first number refers to protection for solid particles in a range of 6 to 0 and the second digit is for protection from liquid ingress on a scale ranging from zero to 9.
Operational Temperature
Operating temperature defines the range of temperatures within which the headphone performs correctly. Any operation out of the range (either excessively cold, or hot) could result in a poor performance, and may even cause damage.
Be sure to ensure that your headphone be within the operating range to ensure maximum performance
Storage Temperature
The temperature range for storage is the manufacturer-defined safe zone within which the headphone is able to be kept.
It’s also unlikely that your headphone will suffer harm if it’s stored outside the range. The purpose of this standard is more to safeguard manufacturers in event that too cold or hot storage can alter your headphone’s performance in any manner.
System Requirements
Some headsets and headphones (USB kinds) are specifically designed for direct connection to computers.
System requirements are the specifications of the computer required for optimal functionality between the USB headphone/headset and computer.
Dimensions
The dimensions specification in the specification is the maximum size, length, and width of the headphone, when it is worn correctly.
This specification could be modified by expanding the headphones or collapsing them. This is why it’s rarely listed in headphone specifications sheets.
The majority of the times when measurements are mentioned they are referring to the size of the packaging for the headphones.
Packaging
The specifications for packaging typically state what dimensions will be included in the box the new headphone is expected to arrive in.
Warranty
The warranty or guarantee is written promise given to the buyer of the headphones by the manufacturer, which promises to fix or replace it when needed within a specific duration of.
The warranty description could inform the buyer of a couple of important information about the warranty provided from the producer:
- What is the length of time that the manufacturer’s warranty is valid for the headphones they just purchased?
- The warranty is invalid if the headphones are purchased used
- What warranty coverage will it include and what it will not
- Other limitations to the warranty
- If there are any steps required to get an insurance policy (product Registry, for instance)
A lot of specifications sheets simply mention the time the warranty is valid for. A deeper search is often required to uncover the rest of the details.
Part Number
Some manufacturers will include an item’s part code or the identification number of their product.
Included Accessories
The accessory “specification” lists out the other accessories that will be included with the headset.
The accessories listed are typically:
- Manuals & Guides
- Cable(s)
- Carrying cases
- Adapters
- Chargers
- Charging cables
- Extra ear pads
Be aware that purchasing second-hand equipment doesn’t guarantee that all the accessories included will be included!
Headphone Examples For This Article
The best examples are always the ones that work. As mentioned there are plenty of headphones that have numerous specifications that describe them.
In the course of writing the article I’ve given specific specifications for a range of headphones that are in use.
The specifications mentioned in this article are available in the specification sheets (and pages for the product) of the headphones listed below:
Circumaural Closed-Back Headphones
The Sennheiser HD280 Pro is a circumaural (over-ear) closed-back pair of headphones.

Link to review specs of Sennheiser HD280 Pro.
- Color:black
- Style of wear:Headband
- Resonance to frequencies (Headphones):8 – 25000 Hz
- SPL: Sound Pressure (SPL):113 dB
- THD Total harmonic distortion:0.1 percent
- Contact Pressure:6 N
- Ear couplingcircumaural
- Plug for Jack:3.5 / 6.3 mm stereo
- Cable for connection:Coiled cable (min. 1.3m / max. 3m)
- Transducer Principle:dynamic, closed
- Weight with no cable285 g
- Impedance nominal:64 O
- Rated load:500 mW
- What’s inside the Box:
- One pair HD 280 PRO headphones
- 1 screw-type adaptor for 1/4″
Supra-aural Open-Back Headphones
The Grado Labs SR80e is a supra-aural (on-ear) open-back pair of headphones.

Link to review the specifications for Grado SR80e.
- Transducer TypeDynamic
- Operating Principle: Open Air
- The Frequency Response is20 up to 20.000 Hz
- SPL 1mW99.8 dB
- Maximum Impedance32 ohms
- Driver Matched : .1 dB
- Inside the Box:
- Headphones
- Warranty
- Grado story-sheet
- 6.5mm Golden Adapter
Bluetooth Wireless Headphones
The Master and Dynamic MW60 is a Bluetooth wireless headphone that has an integrated microphone.

Link to review the Master and Dynamic MW60 specs.
- Model: WM60
- Dimensions200mm by 185mm, 50mm
- Drivers: 45mm Neodymium
- Impedance: 32 ohms
- Weight: 345g
- Material:Premium grain leather, lambskin leather, aluminum, stainless steel
- Cable:
- The cable can be detachable. 1.25m Standard Cable
- Micro USB Input Cord
- Headphone Connection: 3.5mm Passive Audio input micro USB charging/firmware update input
- Ear CouplingCircum-aural /Over-Ear
- The type of microphone:Omni-directional
- AntennaMachined aluminum
- EarpadsDetachable lambskin memory memory foam
- Bluetooth Profile Bluetooth 4.1 using Aptx(tm) audio in high-quality
- Inside The Box
- Headphones
- Canvas Headphone Pouch
- Canvas Cord Case
- 1.25m Standard Cable
- Leather Cable Box
- Micro USB Charging Cable
- 3.5/6.3mm Gold-Plated Adapter
True Bluetooth Wireless Earphones
The Klipsch T5 is a pair of wireless Bluetooth headphones.

Link to read the Klipsch T5 specifications sheet.
- style:In-Ear Monitor
- Designer of the Driver:Dynamic Moving Coil Micro Speaker
- driver diameter:5.0 mm
- Mic/RemotecVc 8.0 Quad-mic
- Resonance to Frequency:10Hz-19kHz
- Noise Isolation: -22dB
- Connectors for input:Bluetooth
- (Earpieces): 55 mAh Battery (Earpieces):55 mAh
- Batterie (Charging Cover):360 mAh
- Bluetooth(r) Specifications:
- VersionBluetooth 5.0
- ProfilesA2DP 1.3 and AVRCP 1.6 HFP 1.2 HFP 1.7
- A2DP Codecs: SBC, AAC(r), aptX(r)
- The range:Up to 10m (33ft.)
- The input rating is5V DC 1.0A
- The Status of the Battery:iOS and Android’s Battery Status Monitor
- Weight:
- 96.9g (charging case)
- 5.5g (earphone)
- Colors: Black
- Dimensions (Packaging):6.8′ H x 4.4 W x 1.9″
Earphones
It is the Sennheiser CX 2.00i is a pair of earphones that have an in-built microphone.
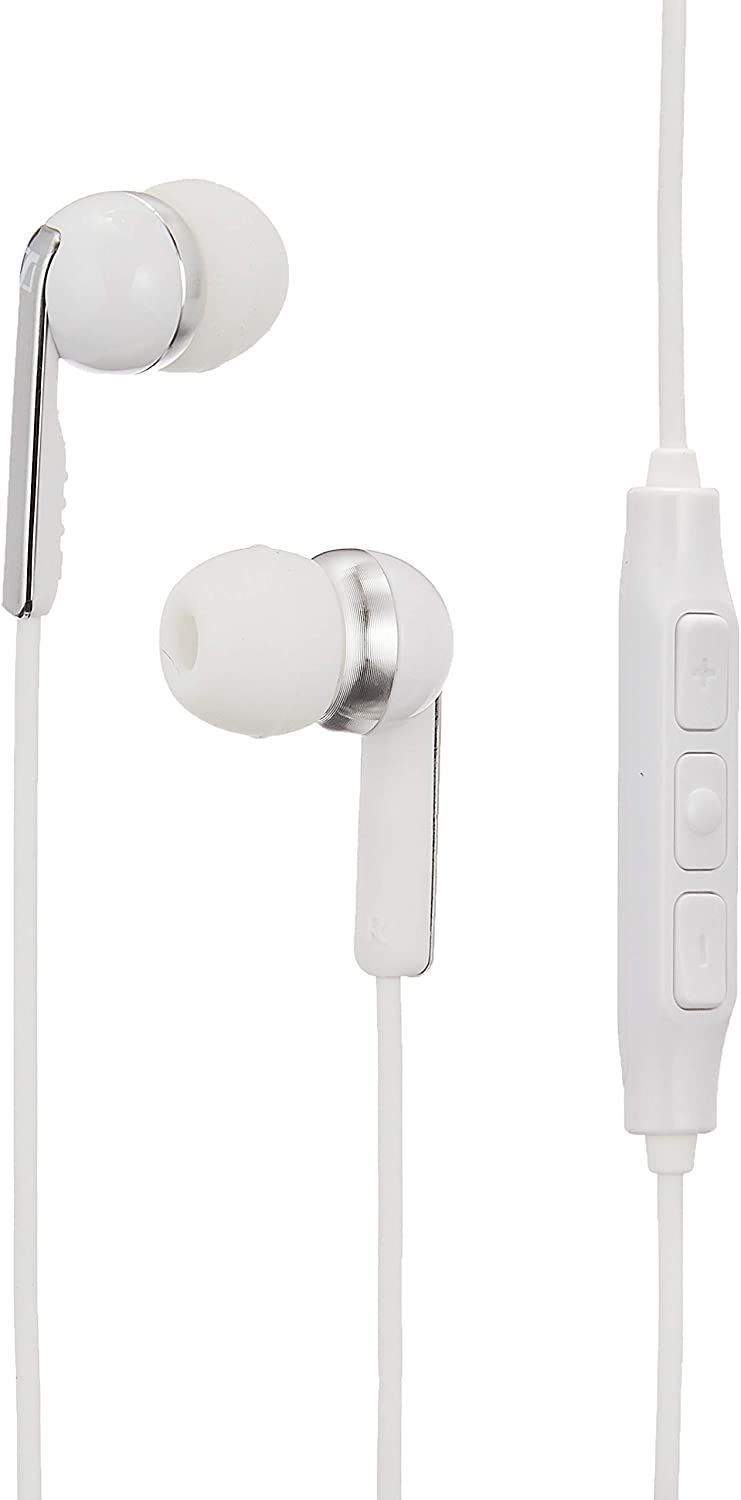
Link to view this Sennheiser CX 2.00i specification sheet.
- General Information:
- Ear Coupling: Ear canal
- Principle of Transducers:Dynamic
- Cable length: 1.2 m
- Connector plugs: 3.5 mm plug, angled
- Delivery includes:
- CX 2.00 headset
- Set of ear adapters (XS, S, M L)
- Headphones:
- Response to frequency:17-20,000 Hz
- Impedance: 28 O
- Sound level of pressure:119 dB
- THD: < 0.5 %
- Microphone:
- Response to frequency:100-10,000 Hz
- Pattern of pickup:Omni-directional microphone
- Sensitivity: -42dBv (1kHz)
- Packaging:
- Dimensions of packaging for products (L B W):100 x 35 + 150 millimeters
- Dimensions of the master carton (L B x W):217 x 119 and 151 millimeters
- Dimensions of the master carton (L B W):460 x 259 191 millimeters
- Languages: English, German, French, Spanish, Italian, Dutch, Portuguese
- Guarantee:2 years
Electrostatic Headphones
The STAX SR-009 is an electrostatic headphone.

Link to review the specifications of STAX SR-009.
- Typ: Push-Pull Open Back Circular Electrostatic Headphone
- Resonance to Frequency:5 – 42,000Hz
- Electrostatic Capacitance110pF (including the cable)
- Impedance: 145k O (including cable, at 10kHz)
- Sound Pressure Sensitivity: 101dB / 100V r.m.s. 1 kHz
- Maximum Sound Pressure: 118dB / 400Hz
- Bias Voltage: 580V DC
- Left and right identification:“L” along with “R” are marked on the arch assembly (inside the head spring) Left channel cable is identified with a solid line. Right channel is identified with an dotted Line.
- Ear PadsGenuine Lamb Leather (direct skin contact) High-quality synthetic leather (surrounding part)
- CableSilver-coated 6N (99.9999%) OFC parallel 6-strand special wide-capacity cable with low capacity, 2.5m full length
- weight:1lb with cable 1.3lb with cable
Planar Magnetic Headphones
The HiFiMan Susvara is a planar magnetic headphone.

Links to the HiFiMan Susvara Manual for Users. Manual.
- The Frequency Response is6Hz-75kHz
- Impedance: 60O
- Sensitivity: 83dB
- Weight: 450g (15.9oz)
- Contents of the Package:
- (1) Headphones in a pair
- (1) 3m headphone cable (4-pin XLR plug)
- (1) 3m headphone cable (6.35mm plug)
- (1) One pair of earpads (mounted on the headphone)
- (1) Owner’s Guide for Owners
Balanced Armature IEM Earphone
Shure SE535 is a pair of in-ear monitors with balanced armature.

Link to review details of Shure SE535.
- Transducer type: Triple balanced-armature drivers
- Sensitivity (at 1 khz):119 dB SPL/mW
- Impedance (at 1 kHz):36 W
- Frequency Range: 18 Hz – 19.5 kHz
- Input connector: 3.5mm (1/8 in.) gold-plated stereo connector
- Net weight: 30 g (1 oz.)
- Temperature of operation:-18deg C to 57degC (0deg F up to 135deg)
- Temperature of storage:-29deg C to 74deg C (-20deg F to 165deg F)
- Accessories:
- 1 1 Bluetooth(r) 5. Earphone Communication Cable
- 1 Micro-USB Charging Cable
- 1 -Universal 3.5 mm Earphone Communication Cable
- 1 Soft Flexible Sleeves (S, M, L)
- 1 Foam Sleeves (S, M, L)
- 1 – Yellow Foam Sleeves
- 1. Triple Flange Sleeves
- 1 Premium Carrying Case
Bone Conduction Headphones
Aftershokz Titanium is a well-known example of a headphone that uses bone conduction.

Link to look up details of Aftershokz Titanium.
- Features:
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Settings for EQ
- PremiumPitch+(tm)
- Back-a-track: N/A
- Battery Life:6 hours
- Type of battery:Lithium-ion
- The charge time is2 hours
- Charger: Micro USB
- Command Controls:Yes
- Codecs compatible with HTML0:SBC
- Compatible profiles: A2DP, AVRCP, HSP, HFP
- Resonance to frequencies:20Hz~20KHz
- MicrophoneDual noise-canceling mic
- Microphone Sensitivity:-40dB +- 3dB
- Moisture detector: N/A
- Multipoint pairing: Yes
- Sensitivity: 100 +- 3dB
- Time to standby:10 days
- The band of titanium:Partial
- Typ:Bluetooth 4.1
- Garantie:2 years
- Water resistance: IP55 (water-resistant)
- The weight is36 g
- The range of wireless:33 feet
What’s Inside The Box?
- Titanium Headphones
- Drawstring Carrying Case
- USB Charging Cables
- Earplugs
Headset
The Clear-Com CC-400X4 is a professional headset.

Link to review the Clear-Com CC400-X4 Specifications.
- Features:
- Standard headset with double-ears.
- High-quality dynamic cardioid microphone
- High-adjusted ambient-noise headphones
- Microphone: 300Hz – 20kHz frequency response
- Headphone: 40Hz – 20kHz frequency response
- The cushion is soft and leatherette.
- Flexible gooseneck microphone position
- 300-degree boom mic rotation for the ON/OFF mic-mute switch
- Rugged design
- Headphone:
- Type: Closed-back
- Driver40mm dia., Neodymium magnet and the copper-clad voice coil of aluminum
- Frequency Response: 40Hz – 20kHz
- Open Circuit Sensitivity:
- -61.0 DB +-3.5 dB at 1kHz, the typical
- 99dB + -3 dB (SPL) at 1kHz, the typical
- Impedance200 Ohms + – 30% at 1kHz average
- Microphone:
- Elements:Dynamic
- Polar Pattern: Hyper-cardioid
- Frequency Response: 300Hz – 20kHz
- Impedance200 Ohms +- 30% at 1kHz average
- Cable5ft (1.55m) in length, with an an 8-pin connector at the end of headset; 4 pin Female XLR
- Dimension:
- Packaging for the CC-400:
- 4.8 13.3 x 10.43 inches (122 x 265 x 330 millimeters) WxHxD
- Packaging for the CC-400:
- weight:11.1oz (315g) without 8-pin cable assembly, M3*18mm SCREW
USB Headset
The Logitech H390 is a headset that connects using USB.

Link to look up details of Logitech H390.
- Features:
- USB Computer Headset
- Digital Stereo Sound
- Noise Canceling Mic
- Controls In-Line
- Ear Cups And Headbands Padded
- USB-A Connection
- Dimensions:
- Height x Width x Depth: 200 mm x 245 mm x 72 mm
- The weight is0.197 Kg
- System Requirements:
- Compatible works with Common calling applications that run on nearly every operating system and platform.
- Windows (r) or macOS
- Google OS (tm)
- USB port (Type A port or adapter)
- Input Impedance: 32 Ohms
- Sensitivity (headphone):94 dBV/Pa + 3 dB
- Sensitivity (microphone):-17 dBV/Pa + 4 dB
- Frequency response (Headset): 20 Hz – 20 kHz
- Frequency response (Microphone): 100 Hz -10 kHz
- Cable length: 2.33 m
- ConnectionsUSB-A capable (1.1, 2.0, 3.0)
- The Contents of the Package
- USB Computer Headset
- User documentation
- Warranty: 2-Year Limited Hardware Warranty
- Part No.981-000014
Noise-Cancelling Headphones
The Sony WH-1000XM3 is a pair of active noise-cancelling Bluetooth wireless headphones.

Link to review the specs of Sony’s WH-1000XM3.
- Weight: Approx. 8.99 oz
- Headphone Type Closed
- Dynamic Driver Unit1.57 ” Domes kind (CCAW voice coil)
- MagnetNeodymium
- Impedance:
- 47ohm (1 1 kHz) (when connecting using the headset cable while the unit is switched on)
- 16 Ohm (1 1 kHz) (when connecting with headphones with the unit switched off)
- Diaphragms:Aluminum coated LCP
- The Frequency Response is4 Hz-40,000 Hz
- Resonance to Frequency (Active operation):4 Hz-40,000 Hz
- Frequency Response (Bluetooth(r) Communication):
- 20 Hz-20,000 Hz (44.1 kHz Sampling)
- 20 Hz-40,000 Hz (LDAC 96 kHz Sampling, 990 kbps)
- Insensitivities (dB/mW):
- 104.5 dB/mW (1 KHz) (when connecting using the headphone cable while the unit is in the on position)
- 101 dB/mW (1 KHz) (when connecting using headphones with the unit off)
- Volume ControlTouch Sensor
- Cord TypeSingle-sided (detachable)
- Cord Length: Headphone cable (approx. 3.94 ft, OFC strands, gold-plated stereo mini plug)
- PlugGold-plated Mini stereo plug with L-shape
- Input: Stereo Mini Jack
- Style of Wearing:Circumaural
- NFCYes
- HX DSEE:Yes
- “Passive Operation”:Yes
- Battery:
- Cost TimeApprox. 3 hours (Full charge)
- Method of Battery Charge:USB
- The Battery’s Live (Continuous Recording Time):
- Max. thirty hours (NC ON)
- Max. 38 hours (NC Off)
- The Life of the Battery (Waiting for):
- Max. thirty hours (NC ON)
- Max. 200 hours (NC Off)
- Bluetooth(r):
- Version:Version 4.2
- Effectual Range:Line in sight about. 30 feet (10 m)
- Frequency Band:2.4 GHz band (2.4000-2.4835 GHz)
- Profil:A2DP, AVRCP, HFP, HSP
- Supported Audio Format(s): SBC, AAC, aptX, aptX HD, LDAC
- Supported Content Security:SCMS-T
- Noise Canceling:
- Off/On SwitchYes
- personal NC optimizer:Yes
- Atmospheric Pressure Optimization:Yes
- Ambient Sound Mode: Yes
- Attention:Yes
- Color Choices:Black or Silver
- What’s Inside The Box:
- Carrying Case
- Plug Adaptor for In-flight Use
- Headphone cable (approx. 47 1/4” [1.2 m])
- USB cables: Type-C(tm) (approx. 7 7/8” [20 cm])
Selecting the best headphones or earphones to suit your needs and budget can be a difficult task. That’s why I’ve put together
You can use it to assist in making your decision on the best headphones or earphones to purchase.

Hey there mobile audio lovers! My name is Darlene R, founder and chief editor at headphonesfans.com. Ask any mobile audio fanatic, installer, or company rep what makes a good car speaker, sub or amp, or, better yet, why he or she prefers a certain brand over another, and be prepared to endure a litany of opinions, viewpoints, and passion-fueled perspectives. To be honest, mobile audio shopping can be a daunting task without a guide, so I’ve assembled what I feel are the best products to consider to make things easier for you. Welcome headphonesfans.com!













